1.Process management
process: a prog in executation eg: a word processing program, sending o/p to a printer etc.
a program is a passive entity a process is an active entity
-
functions assosiated with process management
-
Scheduling process and threads on the CPU (since there will be more than one process running)
-
Creating and deleting both user and sustem processes
-
suspending and resuming processes
-
providing mechanisms for synchronization
-
Providing mechanisms for process communicatino
-
all these are done through system calls
2.Memory management
Mani memory is a large array of bytes ther arises the needfor memory management Instructions must be in memory fo rexections
-
Functions associated with memory management
-
allocation and deallocation of memory space
-
keep track of which parts of memory are currently being used and who is using them
-
deciding which data to move in and out
-
3. Storage management
1.file amanagement
-
when multiple users tyr to access file, OS will control which user may access a file and how that user may access (eg: read, write, appedn)
-
Functions associated with file management
-
creating and deleing derectories to organize files
-
Supporting primitives for manipulating files and directories
-
Mapping files into secondary storage
-
Creating and deletin file backing up files on stable storage media
-
2.Mass storage maangement
the computere system provides secondary storage to back up main memory
-
Function with secondary storage management
-
Free-space management
-
Storage allcoation
-
Disk scheduling
-
-
FUctions with tertiary manaagement
-
Mounting and unmounting media in devices
-
Allocations and freeing the devices for exclusive use by process
-
Migrations data from secondary to tertiary storage
-
3. Catching
used for fast retrival of data
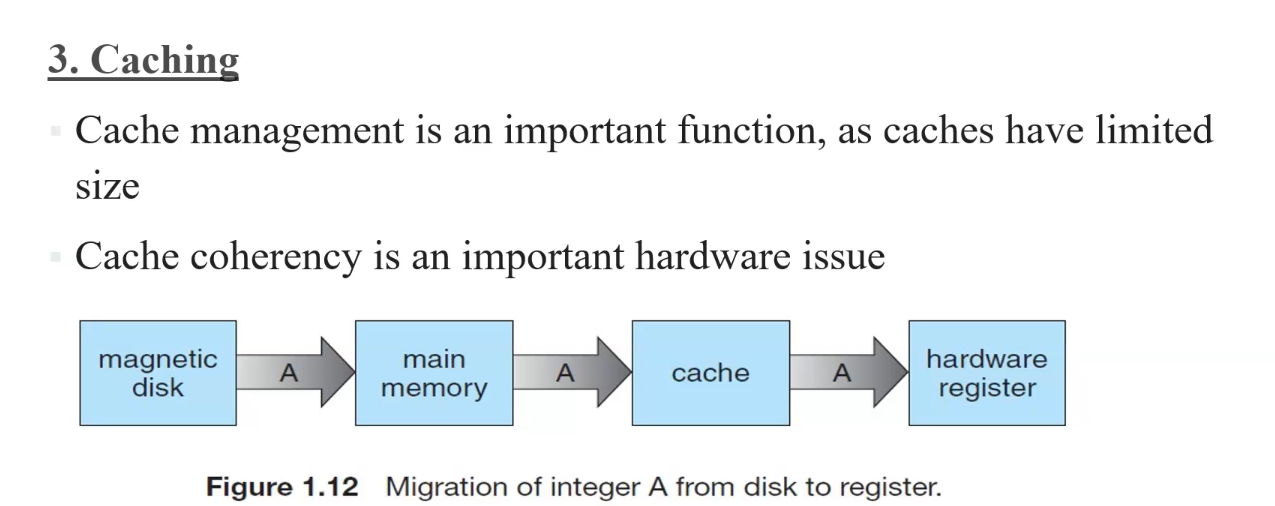
when updationn occurs in any part f the memory evry part should be updated ,its called cache coherency
spoolig : temperary data storage mechanism, stored in secondary storage devices
buffering : usees area inside the main memory
4.I/O systems
act as an interface b/w user and system
-
a general device-friver interface
-
driivers for specific hardware devices
-
a memory -management component htat includes buffering, caching, and spooling (*spooling taking space from the disk,used with data transfer b/w input output devices *buffering does not have a huge maount space, )
5.Protection and security
-
Mechanism for controlling the access of processes or users to the resources deefined b a comp system
-
an unprotected resource cannot defend against use by an unauthorized or incompetent user
-
A protection-oriented system provides a means to distinguish b/w authorized and unauthorized usage